BECE 2011 Social Studies Past Questions and Answers
Answer all questions in this section.
Each question is followed by four options lettered A to D. Find the correct answer for each question.
1. The purpose of naming ceremonies in traditional Ghanaian homes, is to
Solution: Naming ceremonies in traditional Ghanaian culture serve the primary purpose of giving the child an identity within the community and family. This ceremony formally introduces the child to society and assigns them a name that connects them to their heritage and cultural identity.
2. Which of the following officials are not elected through general elections in Ghana?
Solution: Ministers of state are appointed by the President and approved by Parliament, rather than being elected through general elections. Members of Parliament, the President, and Assembly members are all elected positions chosen by voters.
3. Festivals are important in Ghana because they enable the people to
Solution: Festivals in Ghana serve as cultural celebrations that help preserve history and allow people to remember and commemorate important past events, traditions, and cultural heritage of their communities.
4. The instrument used in measuring the rate of evaporation is
Solution: A hygrometer measures humidity and can be used to determine evaporation rates by measuring the moisture content in the air. A barometer measures atmospheric pressure, an anemometer measures wind speed, and a hydrometer measures liquid density.
5. In which vegetational belt is Ghana's cocoa mostly grown?
Solution: Ghana's cocoa is primarily grown in the semi-deciduous forest zone, which provides the ideal climate conditions with adequate rainfall and forest cover that cocoa trees require for optimal growth.
6. Equal hours of day and night are experienced in Ghana when the sun is overhead on
Solution: Equal hours of day and night (equinox) occur when the sun is directly overhead at the Equator (Latitude 0°). This happens twice a year during the spring and autumn equinoxes.
7. One of the aims of the African Union (AU) is to
Solution: The African Union was established with the primary aim of promoting peace, security, and stability on the continent, which includes eliminating conflicts in Africa through diplomatic means and peacekeeping efforts.
8. The eagles in Ghana's Coat of Arms signify
Solution: The eagles in Ghana's Coat of Arms symbolize the protection of the people and the nation's vigilance in safeguarding its citizens and sovereignty.
9. The head of government of the second Republic of Ghana was the
Solution: During Ghana's Second Republic (1969-1972), the country operated under a parliamentary system where the Prime Minister served as the head of government, while the President was the ceremonial head of state.
10. Which of the following oceans lies between Africa and America?
Solution: The Atlantic Ocean is located between Africa and America (both North and South America), serving as the major water body separating these continents.
11. Ghana can minimize the importation of goods mainly by
Solution: Increasing taxes on imports (tariffs) makes foreign goods more expensive, encouraging consumers to buy locally produced alternatives and thereby reducing the volume of imports.
12. An important source of locally generated revenue for District Assemblies in Ghana is
Solution: Market tolls collected from traders and vendors in local markets represent a significant source of internally generated revenue for District Assemblies, as they have direct control over local market operations.
13. Indecent dressing among the youth should be discouraged because it
Solution: Indecent dressing is discouraged primarily because it causes individuals to lose their dignity and self-respect, which are important values in maintaining personal character and social standing.
14. The Domestic Violence and Victims Support Unit (DOVVSU) in Ghana is responsible for resolving problems relating to
Solution: DOVVSU is specifically established to handle domestic violence cases and issues related to family welfare, including protecting victims of domestic abuse and supporting their rehabilitation.
15. Ghana's high indebtedness to foreign countries can be reduced by
Solution: Using locally produced goods reduces the need for imports, thereby saving foreign exchange and reducing the country's dependence on foreign borrowing to finance imports.
16. One major reason for the migration of ethnic groups into modern Ghana was the search for
Solution: Throughout history, ethnic groups migrated into the area that is now Ghana primarily in search of better economic opportunities and means of livelihood, including fertile land for farming and trading opportunities.
17. Laws are mainly made to ensure
Solution: Laws are primarily created to ensure social conformity by establishing standards of behavior that all members of society must follow, thereby maintaining order and harmony in the community.
18. Public corporations are set up by the government mainly to provide
Solution: Public corporations are established by the government primarily to provide essential utility services such as electricity, water, telecommunications, and transportation that are crucial for national development.
19. The most important factor that can help improve productivity in state enterprises is
Solution: Proper supervision ensures that workers are guided, monitored, and supported in their tasks, leading to better performance, accountability, and overall productivity in state enterprises.
20. Floods in our communities can best be controlled through
Solution: Planned layout of communities, including proper drainage systems, appropriate building locations, and flood-prone area management, is the most effective way to control flooding.
21. The interpretation of the constitution of Ghana is a function of the
Solution: The judiciary, particularly the Supreme Court, has the constitutional responsibility to interpret the constitution and determine the meaning of constitutional provisions when disputes arise.
22. Free movement of people, goods and services is one of the main aims of the
Solution: ECOWAS (Economic Community of West African States) was established with the primary aim of promoting economic integration, including the free movement of people, goods, and services among member countries.
23. Industries must be located outside residential areas to
Solution: Industries are located away from residential areas primarily to avoid pollution (air, water, noise, and soil pollution) that could harm the health and well-being of residents.
24. Which of the following vegetation types experiences high temperature and heavy rainfall throughout the year?
Solution: Tropical rainforests are characterized by consistently high temperatures and heavy rainfall throughout the year, creating ideal conditions for dense vegetation growth.
25. The state can promote the growth of private enterprises by
Solution: The state can support private enterprise growth by organizing training sessions for managers, which improves their skills, knowledge, and capacity to run businesses more effectively.
26. When the scale of a map is expressed in the form of a ratio, it is known as
Solution: When a map scale is expressed as a ratio (such as 1:50,000), it is called a representative fraction, showing the relationship between map distance and actual ground distance.
27. The main reason for encouraging farmers in Ghana to produce more cocoa is to
Solution: Cocoa is one of Ghana's major export crops, and increasing production generates more foreign exchange earnings, which is crucial for the country's economic development and international trade balance.
28. Which of the following is not a product of the forest zone in Ghana?
Solution: Shea nut is primarily found in the savanna regions of northern Ghana, not in the forest zone. Palm nut, cocoa, and coffee are all products of Ghana's forest zone.
29. One moral value that is stressed during an outdooring and naming ceremony of a child is
Solution: During outdooring and naming ceremonies, truthfulness is emphasized as a fundamental moral value that the child should embody throughout their life, alongside other virtues.
30. The tertiary sector of the Ghanaian economy provides
Solution: The tertiary sector, also known as the service sector, provides various services such as banking, education, healthcare, transportation, and tourism rather than producing physical goods.
31. The Djebobo and Torogbani mountains are located in the
Solution: The Djebobo and Torogbani mountains are part of the Akwapim-Togo mountain ranges, which extend through the eastern part of Ghana into Togo.
32. Productivity in the mining sector can be increased in Ghana through
Solution: Modern technology in mining, including advanced equipment and techniques, significantly increases productivity by enabling more efficient extraction, processing, and safety measures.
33. One main reason for the abolition of the slave trade was
Solution: The slave trade was abolished primarily due to growing recognition of its inhuman nature and the moral objections raised by abolitionists who highlighted the cruel treatment of enslaved people.
34. The first African country to allow herself to be assessed under the New Partnership for African Development (NEPAD) was
Solution: Ghana was the first African country to voluntarily submit to the African Peer Review Mechanism (APRM) under NEPAD, demonstrating its commitment to good governance and democratic principles.
35. The African Union (AU) was officially launched on 9th July, 2002 in
Solution: The African Union was officially launched on July 9, 2002, in Durban, South Africa, replacing the Organization of African Unity (OAU) with broader objectives for African integration.
36. One problem hindering the effective functioning of District Assemblies in Ghana is
Solution: District Assemblies face significant challenges in mobilizing adequate funds for development projects, as they rely heavily on limited internal revenue generation and irregular transfers from central government.
37. Which of the following economic activities does not cause deforestation in Ghana?
Solution: Fishing is an aquatic activity that does not involve cutting down trees, unlike crop growing (which requires clearing land), lumbering (direct tree cutting), and charcoal burning (which requires wood).
38. A major effect of lateness to school and work is that it
Solution: Lateness to school and work directly reduces productivity by decreasing the effective time available for learning or working, leading to poor performance and reduced output.
39. Which of the following business units raises its capital through the sale of shares?
Solution: Joint-stock companies raise their capital by selling shares to investors, who become shareholders with ownership stakes in the company proportional to their shareholding.
40. One benefit that Ghana derives from co-operating with international bodies is
Solution: Technology transfer is a major benefit Ghana receives from international cooperation, as it gains access to advanced technologies, expertise, and knowledge that support national development and economic growth.
1. Study the vegetation map of Ghana below and use it to answer the questions that follow:
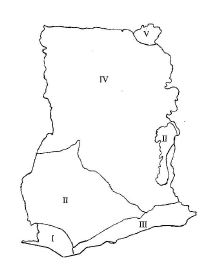
1. (a) Identify the vegetation types numbered on the map as follows: I, II, III, IV and V
(b) Highlight five benefits of water bodies in Ghana.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 1
1.(a) Vegetation types:
I - Tropical Rain Forest
II - Semi-deciduous forest
III - Coastal scrub and grassland
IV - Guinea savanna
V - Sudan savanna
1.(b) Benefits of water bodies in Ghana:
(i) Means of Transportation - Canoes, boats, ferries, etc are used to transport persons and goods on certain rivers, lakes and the sea.
(ii) Source of Water for Domestic Purposes – People fetch water from streams, rivers, ponds, etc, for domestic uses, such as bathing, cooking, washing, and drinking. The Ghana Water Company also gets water from our rivers and lakes for treatment and supply as potable water
(iii) Source of Water for Industrial Purposes – Certain industries rely on water from water bodies for some of their industrial operations
(iv) Source of Food (Fish / Protein) – Fishermen in Ghana obtain fish from our streams, rivers, lakes, lagoons, ponds and the sea.
(v) Source of Employment – Water bodies provide employment and therefore income both directly and indirectly to people such as fishermen, tour guides, Volta River Authority workers, farmers, etc.
(vi) Generation of Hydroelectric Power – The Akosombo dam generates electricity for the entire country using water from the Volta River. The Bui dam, also for generation of hydroelectric power is still under construction.
(vii) Tourist Attraction Sites – Certain rivers and lakes serve as tourist attractions, which help to generate income and foreign exchange for the country.
(viii) Salt Production from Sea Water – Salt can be obtained from sea water through evaporation
(ix) Irrigation of Farmlands – In areas where there is little or no rainfall, farmers rely on water bodies to grow their crops
(x) Drainage System to Prevent Flooding - When rain falls, the water runs into gutters / drains, which carry them into water bodies. This prevents flooding of communities, which could have caused destruction of life and property.
(xi) Habitat for Aquatic Organisms – Several organisms and micro organisms in the ecosystem live in various water bodies
(xii) Source of Minerals – Certain rivers have mineral deposits in them, eg, alluvial gold in Rivers Birim, Pra and Offin, alluvial diamond in the Birim River. Currently, crude oil is drilled from beneath the sea (off shore Western Region)
(xiii) Helps in Rain Formation – Large amounts of water vapour in the atmosphere come from water evaporation from the surface of water bodies. The water vapour rises higher, becomes cooler, condenses and falls as rain.
2. (a) What is cultural change?
2. (b) Explain four factors responsible for cultural change in Ghana.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 2
2.(a) Cultural change: The gradual alteration or adaptations that occur in the way people live. It includes changes in dressing, language, food, clothing, music, religion, beliefs, values, festivities and other expressions of culture
2.(b) Factors responsible for cultural change in Ghana:
(i) Migration - Migration refers to movement of persons or groups of people from a place to settle in another place, either temporarily or permanently. When this happens it may affect the way they do things due to the difference in culture / natural environment of the new place. Eg a person who moves from a warm climatic region to a colder one may be compelled to change his/her dressing from light and scanty clothes to heavier body covering ones.
(ii) Education - Both formal and informal education is aimed at changing one's way of doing things as a result of acquired knowledge, skills and attitudes. As people learn, they acquire new knowledge, which tends to change the way they think / perceive things, which usually leads to a change in the way they live and therefore a change in culture. Eg, change in one's diet due to knowledge of importance of taking balanced diet.
(iii) Religion - One's religion usually defines what is acceptable or unacceptable. Different religions have different belief systems which impact on the way the followers live. For instance, people who change their religions may be compelled to also change the way they dress, the songs they can sing or listen to, the way they pray, sometimes the food they can eat or even the language they speak.
(iv) Urbanisation - People who move from rural areas to urban areas experience drastic changes in the way things are done. As time goes on, they forget about their old belief systems, values and traditional ethics. They now adopt the city lifestyle, which could mean changes in how they dress, how they dance, the songs they sing, the food they eat and even the good manners and polite behaviour they used to have.
(v) New technology and innovation - Swift changes in current technologies and innovative ideas have brought about rapid changes in culture. These changes happen because most of these modern technologies are more interesting, less tiresome, much faster and more user-friendly. Eg, these days, spending days and weeks to clear / plough a piece of land with a hoe / cutlass can now be done in a much better way by a tractor within a few minutes or hours. Children would rather surf the internet, play computer or video games rather than enjoying storytelling. Letter writing has now been replaced by emails, phone calls, text messaging, chatting on social internet networks.
(vi) Inter-marriages - When people marry they usually change some of the way they do things, out of compulsion, mutual understanding or the love they have for their spouses. Eg, they learn how to prepare and eat different kinds of food. There may also be changes in the way they talk, dress, work, worship God, relate with others, etc.
(vii) The Media - Both the print and electronic media play very significant roles in changing cultures of people. The more people see and hear a particular thing / behaviour, the more accustomed they get to that thing / behaviour. With time, these viewers and listeners gradually change from their old cultural ways of doing things to what they have been seeing / hearing. Many times, such changes are actually unconscious – ie, they don't intentionally decide to change, however they suddenly find themselves doing it. Eg, using a swear word (profane language) or unconsciously humming a song one heard on radio / TV.
3. (a) Highlight any four contributions of Ghana to the United Nations Organization
3. (b) In what four ways has Ghana benefited from the United Nations Organization?
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 3
3.(a) Contribution of Ghana to the United Nations Organization:
(i) Peace-keeping operations in war-torn countries (ii) Payment of dues – financial contribution (iii) Human resource contribution – eminent Ghanaians serving at the UNO in various capacities (iv) Sheltering refugees fleeing from their countries (v) Participating in deliberations programmes at the UNO general assembly and other organs (vi) Assisting and facilitating the operations and campaigns of UN specialised agencies such as FAO, WHO, UNICEF, UNDP, UNHCR, etc
3.(b) Ways in which Ghana has benefited from the United Nations Organization:
(i) Loans and grants from the IMF and the World Bank to support development projects (ii) Health delivery services provided by the WHO (iii) International recognition as a result of our membership of the UNO (iv) Rural developmental projects by the UNDP (v) Food and Agricultural developmental programmes by the FAO (vi) Employment of Ghanaians at the UNO and its specialised agencies (vii) Support for Ghana's democracy by supply of international observers during general elections
4. (a) What is separation of powers?
4. (b) Outline four advantages of separation of powers.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 4
4.(a) Separation of powers: The practice where each of the three arms of government work independently of the others (The three arms are the Executive, the Legislature and the Judiciary)
4.(b) Advantages of separation of powers:
(i) It prevents dictatorial tendencies of any arm of government, since absolute power is not given to any one governmental organ (ii) It ensures the rule of law in the governance of the country (iii) It protects the rights and freedoms of the people (iv) It supports specialization of duties, which promotes efficiency (v) It gives room for checks and balances of one arm from the other arms and therefore enhances effectiveness of governance (vi) It reduces corruption and abuse of power
5. In what five ways can Ghana reduce her dependency on foreign financial support?
5. (b) State two reasons why labour is not fully used in Ghana.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 5
5. Ways by which Ghana can reduce her dependency on foreign support:
(i) Supporting local industries to produce more local ('made-in-Ghana') goods (ii) Encouraging industries to add value to primary goods for both local consumption and export (iii) Encouraging Ghanaians to patronise 'made-in-Ghana' goods (iv) Increasing locally generated income by widening the tax net (v) Fighting corruption in order to conserve locally generated funds (vi) Increasing the production of export goods in order to earn more foreign exchange (vii) Investing more in the education of Ghanaians in order to provide higher skilled labour / expertise (viii) Giving indigenous experts and companies that chance to work on specialised projects, which would have been given to expatriates (ix) Granting scholarships to Ghanaians to train in highly specialised fields (x) Providing attractive incentives for local experts to stay and work in Ghana
Solutions for Question 6
6.(a) Ways through which human resource can be developed in Ghana:
(i) Training and retraining – Staff of institutions and other bodies must be given in-service training on a continuous basis in order to update their knowledge, sharpen their skills and positively improved their work attitudes. This would promote efficiency and higher productivity.
(ii) High quality and specialized education – Students must be educated in specialized areas that are relevant to the current economic environment, rather than being given mere classical and theoretical lessons/lectures, which may not be beneficial enough to them nor to the nation.
(iii) Improved working condition – The conditions under which employees work should be significantly improved in order to bring out the best in them. These conditions include the physical, social and political (work policies) environments
(iv) Opportunities for further studies - Organization must create opportunities, scholarship schemes and sponsorships for further studies for their staff based on specified criteria. These would greatly motivate workers to work harder in order to meet the criteria for sponsorship or scholarship awards.
(v) Availability of job opportunities - There is the need for the government and other bodies to create more job opportunities for school leavers. This will enable them to practice what they have learnt, in order to gain experience and perfect their skills.
(vi) Effective monitoring and supervision - Managements of institutions must ensure effective and regular supervision, monitoring, assessment and evaluation. This would keep workers on their toes and motivate them to work more diligently.
(vii) Equitable wages and salaries - It is vital for workers to be paid fair wages and salaries. In this regard, managements should consider paying workers based on performance, rather than on a general basis. If done, this will surely encourage hardworking staff to work even harder and the lazy ones to sit up and work more efficiently.
(viii) Security and welfare services - Every worker desires a certain level of both job and financial security. It is important therefore that worker be given security and welfare services, such as social security scheme, life / fire / motor insurance, staff welfare packages, etc. This helps to put workers' minds at ease, and therefore the peace of mind to focus on their work.
(ix) Award Schemes - As social beings, we all want to be given the recognition where it is due. Institutions in order to further motivate their staff, should consider setting up various award and reward schemes. The selection of winners must be done in the most transparent and objective manner possible, in order to maintain the credibility of the scheme. This should help to inspire workers to put in more for higher productivity.
(x) Use of efficient working tools - In recent times, there has been an emphasis that for greater productivity, there is the need to work smarter, rather than working harder. This simply stresses the need for using efficient modern tools / technology to produce more in less time. Workers using efficient working tools would do more work, as they would enjoy putting in relatively less effort and having greater output.
6.(b) Reasons why labour is not fully used in Ghana:
Insufficient job opportunities
Inadequate training
Lack of effective supervision
Low quality of education
Poor working conditions
Lack of opportunities for further studies
Unfair wages and salaries
Lack of award schemes
Lack of efficient working tools
Inadequate security and welfare schemes